12 Circular Motion (A2)
12.1 Kinematics of Uniform Circular Motion
Radian:
angle subtended at the center of a circle by an arc equal in length to the radius of the circle
Angular displacement:
angle moved by an object in circular motion, expressed in radians
Angular Speed:
rate of change of angular displacement. It is defined as the angle moved per unit time, usually measured in radians per second (rad/s) or ω
-
The relationship between angular speed and the period of the motion is given by ω = 2π/T, where T is the period of the motion.
-
The linear speed of an object in circular motion is given by v = rω, where v is the linear speed, r is the radius of the circle, and ω is the angular speed.
12.2 Centripetal Acceleration
-
Centripetal acceleration is the acceleration of an object moving in a circle due to a force acting towards the center of the circle. It is always perpendicular to the direction of motion of the object.
-
Centripetal acceleration causes circular motion with a constant angular speed.
-
The magnitude of the centripetal acceleration is given by a = rω2, where a is the centripetal acceleration, r is the radius of the circle, and ω is the angular speed.
-
The magnitude of the centripetal acceleration can also be expressed in terms of linear speed as a = v2/r, where v is the linear speed.
-
The centripetal force for an object in circular motion is given by F = ma = mrω2 or F = mv2/r, where F is the centripetal force, m is the mass of the object, r is the radius of the circle, ω is the angular speed, and v is the linear speed.
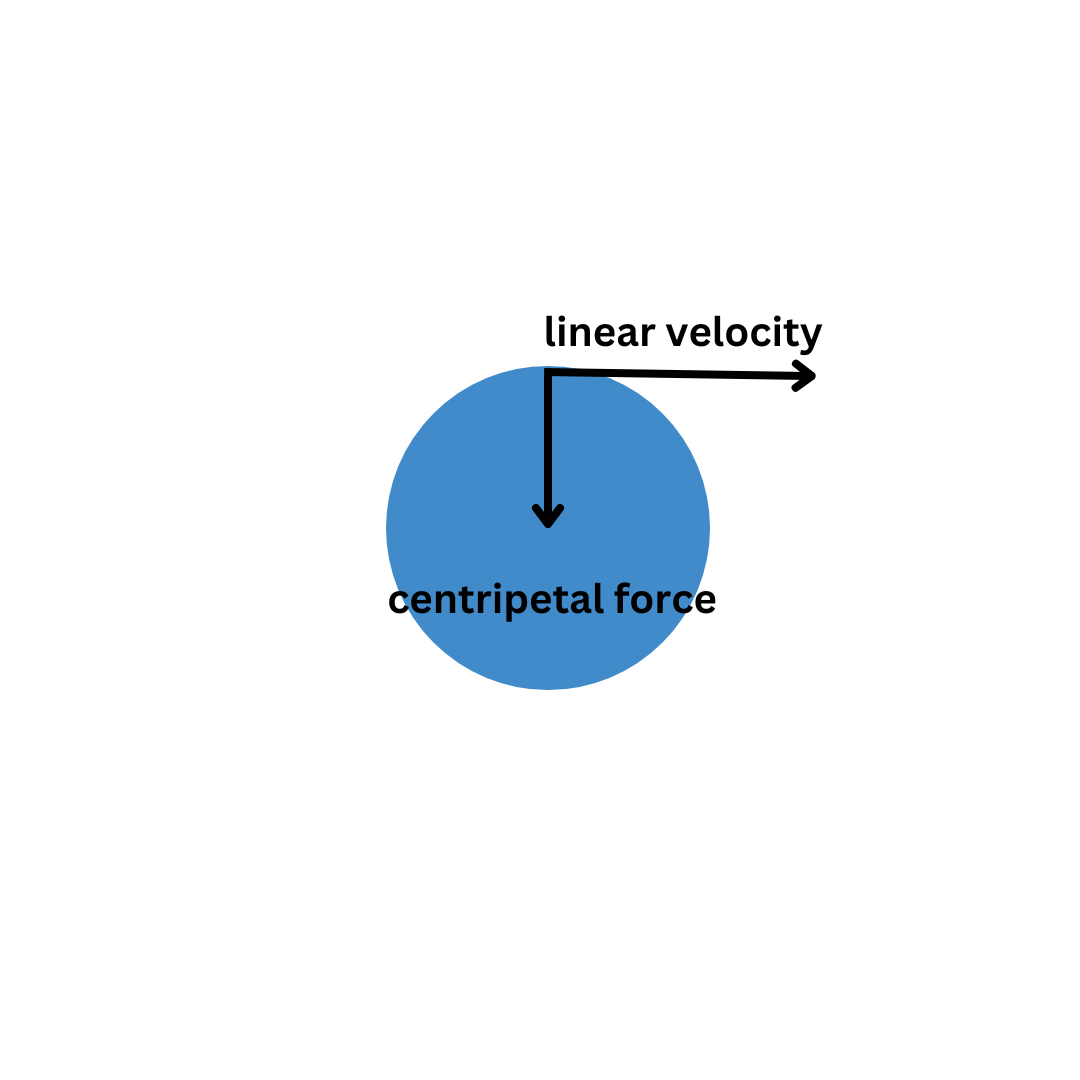 --- difference between linear velocity and centripetal force
--- difference between linear velocity and centripetal force