23 Nuclear Physics (A2)
23.1 Mass Defect and Nuclear Binding Energy
-
Equivalence of Energy and Mass: The equivalence between energy and mass is represented by the equation E = mc².
-
Nuclear Equations: Nuclear equations represent nuclear reactions such as 14N + 4He → 17O + 1H.
Mass Defect:
difference between the sum of the individual masses of nucleons and the actual mass of a nucleus
-
Binding Energy: Binding energy is the energy released when nucleons come together to form a nucleus.
-
Binding Energy per Nucleon: Binding energy per nucleon varies with nucleon number and has a maximum value for nuclei with an atomic mass number of around 56.
-
Nuclear Fusion and Fission: Nuclear fusion is the joining of two lighter nuclei to form a heavier nucleus, while nuclear fission is the splitting of a heavier nucleus into two lighter nuclei.
-
Energy Released in Nuclear Reactions: The energy released in nuclear reactions can be calculated using E = ∆mc².
23.2 Radioactive Decay
-
Random Nature of Decay: The random nature of radioactive decay is evidenced by fluctuations in count rate.
-
Spontaneous and Random Decay: Radioactive decay is both spontaneous and random.
-
Difference between Random and Spontaneous decay: Spontaneous means that a process occurs on its own time scale without external stimulation. Random means that an element of chance is involved somewhere in the process, which means that it is impossible to know exactly when a single C nucleus decays.
Activity:
number of radioactive decays per unit time
Decay Constant:
probability of decay per unit time
-
A = λN is the relationship between activity and the number of radioactive nuclei N.
-
N0 is the number of radioactive nuclei at the start (or the maximum number)
-
Half-life: Half-life is the time taken for half the original number of radioactive nuclei to decay.
-
Relationship between Decay Constant and Half-life: The relationship between decay constant and half-life is λ = 0.693/t(1/2) where t(1/2) is half of the time.
-
Exponential Decay Process: Radioactive decay is an exponential process, and the relationship between activity or number of undecayed nuclei and time is x = x0e(-λt).
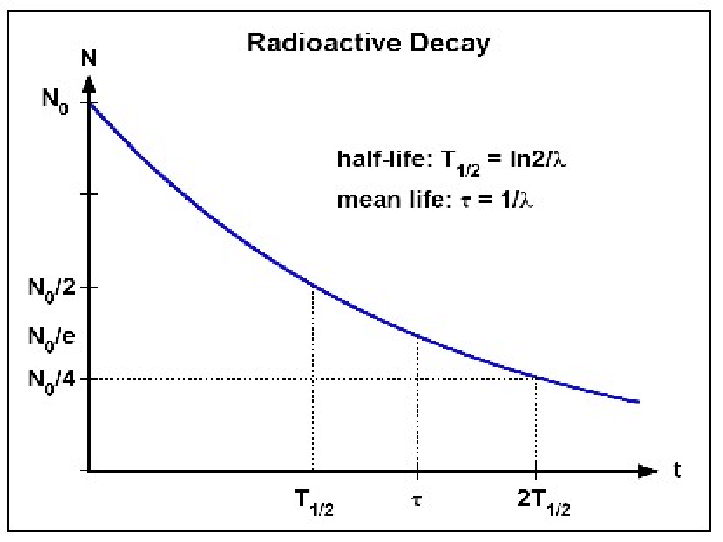 -- Radioactive Decay graph
-- Radioactive Decay graph